Oil and Gas SCADA is Different
Oil and Gas SCADA is hardly a new concept. But if you talk to operators of Oil and Gas companies you will hear such similar frustrations.

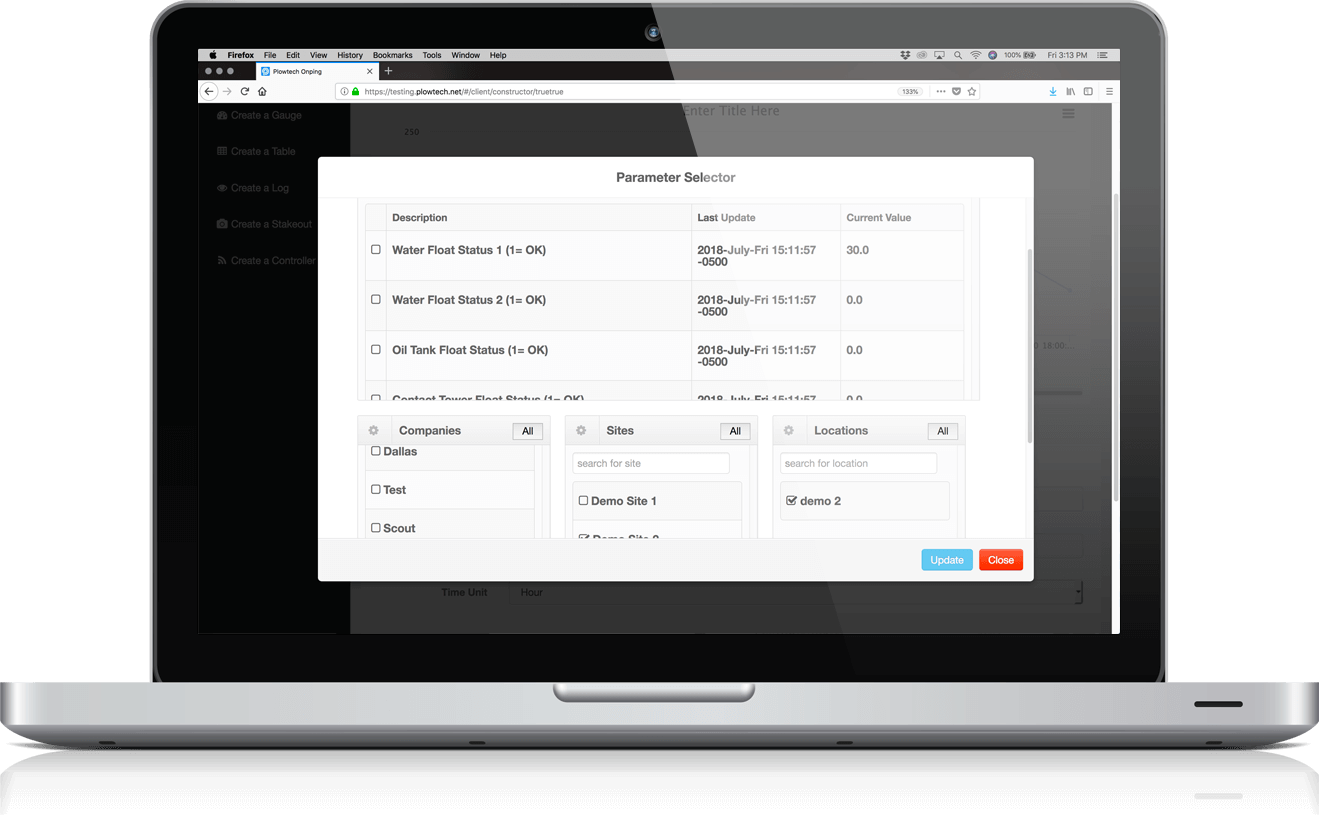
OnPing is designed to be configured and laid out anyway you want. Drag and Drop, low code and intuitive tools allow you to make anything you can imagine.
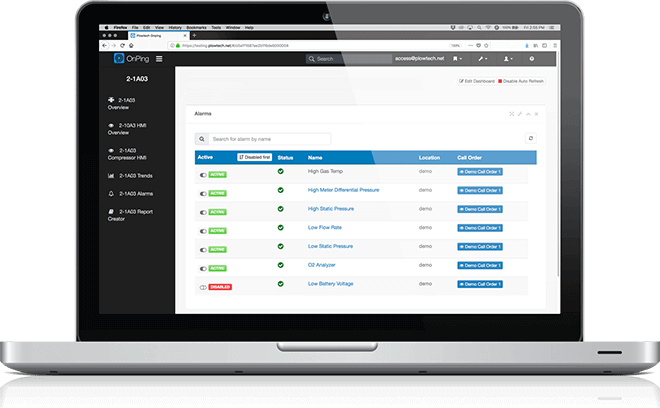
OnPings unique structure makes for more reliable data than traditional Cloud SCADA applications and alarms you can rely on. No matter what, OnPing is watching. We'll also be there for you with 24/7 support and a constantly growing knowledge base of information.
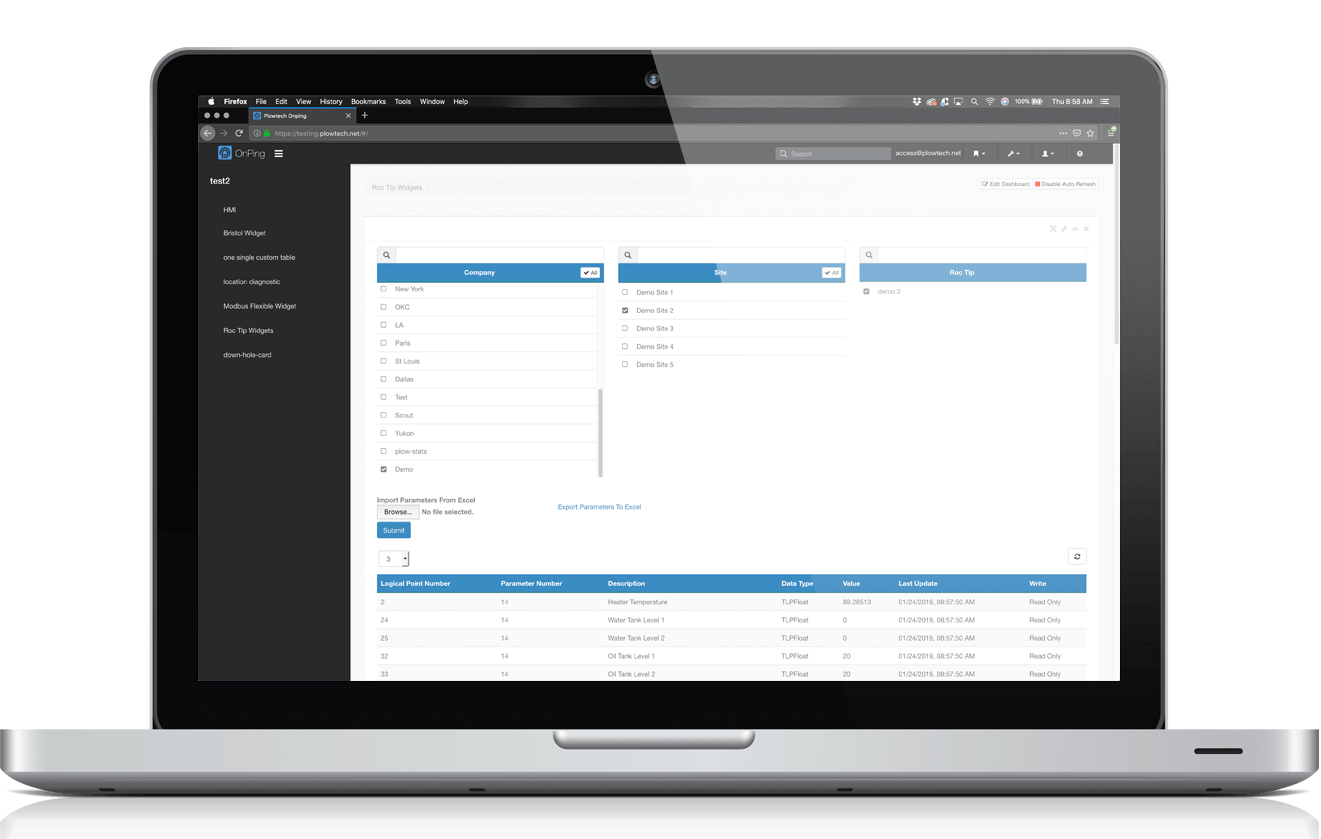
OnPing communicates with hardware from Allen Bradley, Fisher ROC, Schneider, ABB TotalFlow and legacy devices from Bristol Babcock, Ferguson Beauregard plus many more. Any device, any era, OnPing brings it all together in to one powerful modern system.
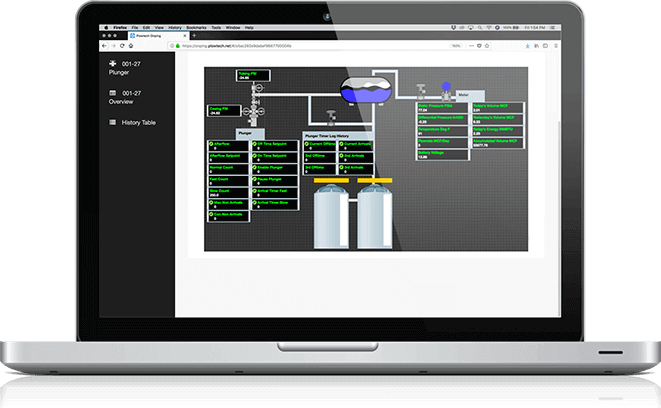
OnPing’s unique structure of cloud SCADA application and advanced on-site Lumberjack Edge Computers produces industry leading speed with real time polling.

Any device, any browser, any time, from anywhere. OnPing’s powerful data and control tools are instantly available anywhere and any time you need them.