OnPing’s User structure can take a bit of getting used to. This document will go through some of the main terminology used to define the relationships between users and groups.
All groups live as part of a big tree. They have parent groups, sibling groups and child groups. If a group is a parent of another group we say it is the “super group” this is one of the terms you define for any group you add.
Almost everything you interact with in OnPing is a member of one group. We will call these things assets. A few common assets in OnPing are Companies, Sites, Locations.
The tree structure of our groups is how the permissions propagate. If you are in a group of an asset you have read but not edit permissions. If you are in a super group of the group an asset belongs to, you have edit permissions.
The other important entity to consider for permissions is the User. Users are the only assets in OnPing that can be members of multiple groups. This is useful if an organization has multiple business units with various levels of visibility required.
Special Notes On Users
Because users are the ones taking actions in OnPing, they take special discussion on permission.
Here is a diagram of the users and groups we will discuss.
Editable Users
When can one user make changes to another? If a user is a member of a group that is super to all of the groups of another then the user in the super group can edit this other user. In our diagram, User A can edit User B and User C. We would call Users B and C editable users for User A.
Assignable Users
A different problem that arises is when a user needs to assign someone to an alarm. Who gets to do that?
If a user is in a group that is super to one of the groups a user belongs to then that user can assign this other user to alarms. In our diagram, User A can assign User B and User C to alarms. User B can assign User C. We would call User C an assignable user for User B.
Notice this is a weaker requirement than Editable Users.
Typical Asset Configurations
Admin Group, User Group
The most common way OnPing is set up is with a company admin group and a company user group.
Below are a few examples of how to configure a. Asset with this setup.
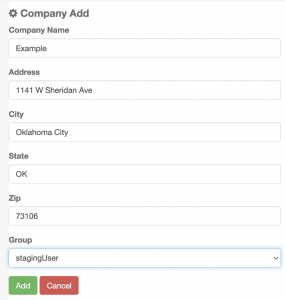
Case 1: Setting up a company, site or location
Companies, Sites and Locations Generally need to be set up as user groups so that all personnel can see them.
Case 2: Setting up an alarm
Alarms are usually set up as Admin. They have a special permission level called edit which they are usually set up with.